Environment - Biomes: Terrestrial
Biomes: Terrestrial
An ecosystem is a functional unit of nature encompassing complex interaction between its biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) components.
Terrestrial Ecosystem
A terrestrial ecosystem is an ecosystem found only on landforms. Six primary terrestrial ecosystems exist: tundra, taiga, temperate deciduous forest, tropical rain forest, grassland and desert.
Major Terrestrial Biomes of the World
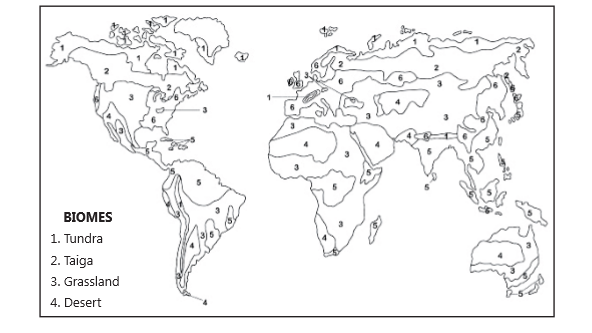

Tundra
Tundra biome is the coldest of all the biomes. It is among the harshest biome and they are found in the arctic region and on top of mountains where the climate is cold and windy and the rainfall is scanty. The tundra regions are covered with snow most of the year and summer brings blooms of wild flowers.
Arctic Tundra Biome
- The arctic tundra is located in the northern hemisphere.
- It encircles the North Pole and extends south to the coniferous forest of the taiga.
- The arctic has cold, desert like conditions.
- The growing season in the tundra region is about 50 to 60 days.
- The average winter temperature is about -34°C, the average summer temperature is about 3 to 12°C, and this enables the biome to sustain life. Rainfall varies in different regions of the arctic.
- There is about 15 cm to 25 cm of yearly precipitation which includes melting snow.
- Soil formation is slow.
- A layer of permanently frozen subsoil known as permafrost exists and consists mostly of gravel and finer material.
- When there is saturation of the upper surface, there may be formation of bogs and ponds which provide moisture for plants.
- In this region there is no deep root system vegetation, though there are a wide variety of plants that can resist the cold climate.
Alpine Tundra Biome
- The Alpine tundra is located on the mountain regions throughout the world, there are at the high altitudes where trees cannot grow.
- The growing season in these regions is about 180 days.
- The temperature during the night is below freezing.
- The soil in the alpine is well drained.
- The vegetation in the alpine tundra is similar to the arctic tundra.
- The vegetation includes plants like tussock grasses, small-leafed shrubs, dwarf trees and heaths.
- The fauna of the alpine tundra are well adapted to its climate, the animals of the alpine include mammals like marmots, pikas, mountain goats, elk and sheep; birds like grouse like birds and insects like butterflies, grasshoppers, beetles, springtails, etc.
Taiga
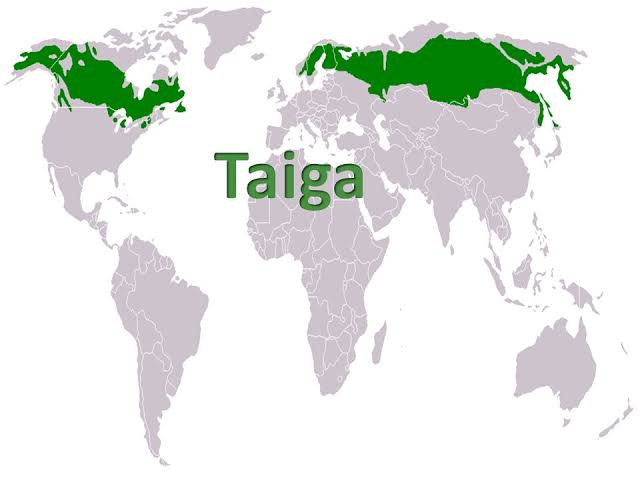
- Taiga is the largest land biome and it makes up of about 29% of the world’s forest cover; a large part of this biome is located in Russia and Canada.
- The boreal forest occurs between 50 and 60 degrees of the north latitudes. It can be found along the broad belt of Eurasia and North America, 2/3rd of it is in Siberia, the rest of it in Scandinavia, Alaska and Canada.
- Taiga is found in the northern parts of North America, Europe and Asia.
- The climate of the taiga is very cold.
- The taiga has a subarctic climate and the temperature ranges between seasons, but the dominant feature of the taiga is the long and cold winters.
- The summers are short, temperature is about 10°C and it lasts around for 1-3 months.
- The winter temperatures are below freezing and reaches and it lasts for five to seven months.
- Throughout the whole year the temperature vary from -54°C to 30°C.
- The summers are short, warm and humid.
- Precipitation in this region varies from 20cm to over 200 cm; the precipitation is mostly in the form of snow. During the growing season the ground is moist.
- The summers have extremely long day length.
- There is explosive plant growth in the summer, and yet the growing season is short and less.
Grassland
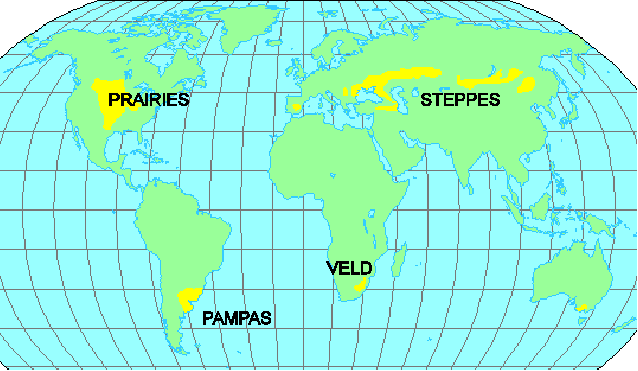
- Grasslands are characterized as lands dominated by grasses rather than large shrubs or trees.
- Very few trees or tall large plants grow in the grasslands.
- Forest or bush fires can also eradicate the sparse tree population.
- The lack of trees is mainly due to soil type and precipitation.
- Grassland biomes are normally situated between a forest and a desert.
- In fact, grasslands surround every desert in Asia.
- Twenty-five percent of the Earth is covered by the grassland biome.
- There is a grassland biome on each continent with the exception of Antarctica.
- Tropical and temperate are the two kinds of grasslands.
- Tropical grasslands experience warm weather all year long while temperate grasslands have hot summers and cold winters.
- Grasslands are perfect for cropping and pasturing because its soil runs deep and is extremely fertile.
- Periodic fires, whether they are human induced or occur spontaneously, are very important to the grassland to ensure that invasive plants do not take over.
Savanna Grassland
- Savanna is grassland with scattered individual trees.
- Savannas of one sort or another cover almost half the surface of Africa (about five million square miles, generally central Africa) and large areas of Australia, South America, and India.
- Savannas are always found in warm or hot climates where the annual rainfall is from about 50.8 to 127 cm (20-50 inches) per year.
- It is crucial that the rainfall is concentrated in six or eight months of the year, followed by a long period of drought when fires can occur.
- If the rain were well distributed throughout the year, many such areas would become tropical forest.
Temperate Grassland
- Temperate grasslands are characterized as having grasses as the dominant vegetation.
- Trees and large shrubs are absent.
- Temperatures vary more from summer to winter, and the amount of rainfall is less in temperate grasslands than in savannas.
- The major manifestations are the velds of South Africa, the puszta of Hungary, the pampas of Argentina and Uruguay, the steppes of the former Soviet Union, and the plains and prairies of central North America.
- Temperate grasslands have hot summers and cold winters.
- Rainfall is moderate.
- The amount of annual rainfall influences the height of grassland vegetation, with taller grasses in wetter regions.
Tropical Rainforest Biome
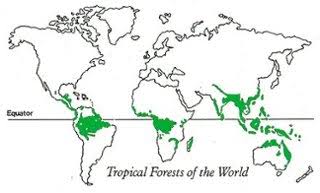
The Tropical Rainforest can be found in three major geographical areas around the world:
- Central America in the Amazon River basin.
- Africa - Zaire basin, with a small area in West Africa; also eastern Madagascar.
- Indo-Malaysia - west coast of India, Assam, Southeast Asia, New Guinea and Queensland, Australia
Characteristics
- Rainforests only cover around 2 percent the total surface area of the Earth, but really about 50 percent of the plants and animals on the earth live in the rainforest.
- Rainforests are found on all of the different continents, except for Antarctica because it is far too cold there for the environment to be conducive.
- Rainforests help to regulate the temperatures around the world and the weather patterns as well.
- Tropical rainforest get lots of rain; in one year they typically receive between 50 and 260 inches (125 to 660 centimeters) of rain.
- The tropical rainforest biome is hot; it has an average temperature of about 77 degrees Fahrenheit (25 degrees Celsius). The temperature never falls below 64 degrees Fahrenheit (17.8 degrees Celsius).
- Tropical Rainforest are extremely humid, due to all the rainfall, the average humidity is between 77 and 88 percent.
- The Amazon Rainforest in South America is the largest tropical rainforest in the world; however these forests are also located in Africa, Central America, Australia, Asia, Mexico and on numerous Caribbean, Pacific, and Indian Ocean islands.
- Tropical rainforest biomes are generally located near the equator; this is why they are said to have an equatorial climate.
Desert Biome
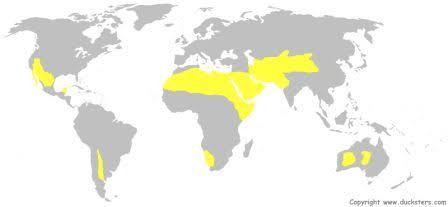
- Desserts are dry or arid areas that receive less than 250 mm of rain each year. Deserts can be hot or cold. They contain plants and animals that are specially adapted to these extremely dry conditions.
Locations
- Hot deserts are located at the Sahara, Arabian, Australian, Australia, Arabian, Peninsula, Mexico/ S.W. USA, S.W. Africa, S.W USA. Others include Argentina, South America, North Africa, Indian, Pakistan and Kalahari deserts.
- Coastal deserts are found at Peru and Chile.
- Cold deserts are located at China, Mongolia, Iran, Afghanistan, S.W Africa, W. China, Argentina, South America, Middle East, Antarctica and USA.
- Semi-arid deserts/ Steppes or moderately dry lands are located at USA, Canada, Ukraine and China.
Deciduous Forest Biome
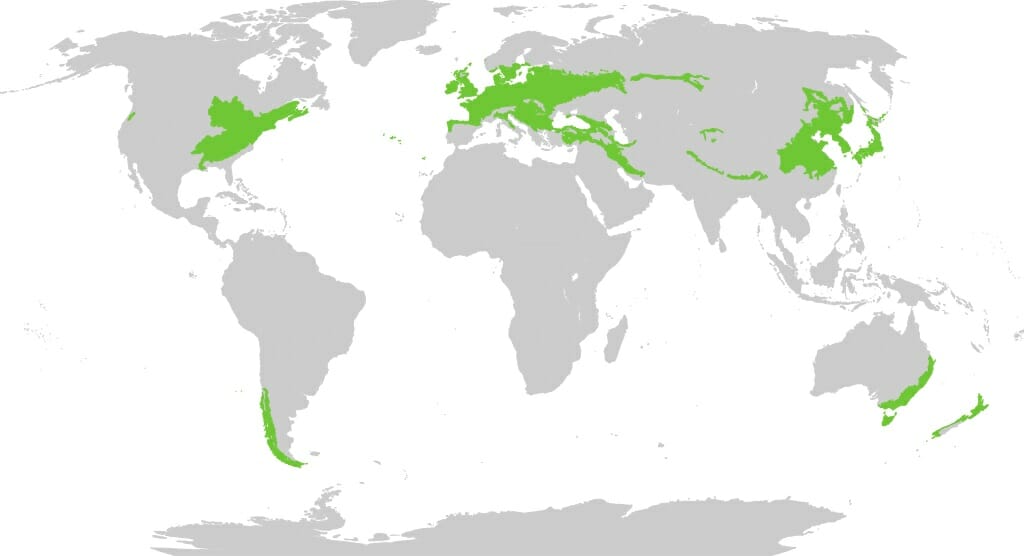
- Forests in which majority of trees lose their vegetative parts, such as leaves, after a particular season are called as deciduous forests.
- A deciduous forest supports diverse ecological types.
- Plants usually grow in the warm temperate climate with abundant moisture and produces new leaves and flowers in spring.
- In summer, long trees support the growth of shade-tolerant trees and plants by casting their shade.
- Leaves fall off in autumn and provide required material for decomposers, soil bacteria.
Tropical Deciduous Forest
Features
- Area has warm summer and moderately cold winter.
- Precipitation is abundant ranging from 75 cm to 150 cm.
- Temperature remains moderate 20 - 27C in summer and - 12C in winter.
- Soil is rich in minerals and organic matter.
- Bamboo, Sal, Shisham, Sandalwood, Khair, Kusum, Mulberry are other commercially important species, grown in most deciduous forests.
- The dry forest is found in areas of rainfall ranging between 100 cm and 70 cm.
Temperate Deciduous Forest
Features
- Temperate deciduous forests can be found in the eastern part of the United States and Canada, most of Europe and parts of China and Japan.
- Temperate deciduous forests get between 30 and 60 inches of precipitation a year.
- Precipitation in this biome happens year round.
- Deciduous forests have a long, warm growing season as one of four distinct seasons.
- There is abundant moisture. The soil typically is rich.
- The leaves dropped from trees provide a steady source of organic material for the soil.
- Many species live in the soil and break down the organic matter.
- Tree leaves are arranged in strata: canopy, understory, shrub, and ground.
- A great deal of light is therefore filtered out before it reaches the ground.
- With the dropping of their leaves during one season, trees stop photosynthesis and enter a dormant period.
- Three main types of trees are characteristic of these forests: northern hardwood, central hardwood, and southeast pine and oak.
No comments:
Post a Comment